Automatically prevents dangerous software from running, keeping your business data safe from malware and cyber threats.
Get free support and training from the US, ensuring you have reliable help available to tackle any technical challenges promptly.
Choose which apps can operate and block the rest, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and ensuring only safe, necessary software runs.
Control your computers from any location, enhancing flexibility and ensuring continuous operations, even when you're away.
Maintain a comprehensive inventory of your network's software, helping you manage licenses and avoid unnecessary expenses.
Receive immediate alerts about problems via email or text, allowing you to respond quickly to potential issues and minimize downtime.
Restrict access to external drives and folders for added security, protecting sensitive data from theft or accidental exposure.
Regularly checks to ensure smooth device operation, preventing disruptions and extending the lifespan of your hardware.
Extra safeguards for the most vulnerable areas of your system, securing remote connections and protecting against intrusions.
Easily update apps to eliminate security risks, keeping your systems secure against the latest threats by patching vulnerabilities promptly.
A detailed review of the security and performance of your devices
Remotely shut down or restart your devices, saving energy and ensuring systems are refreshed and ready for business.
Simplify file transfers to and from your computer, enhancing productivity by making it easier to access and share important files.
Real-time automated application allowlisting provides default-deny protection against unknown malware, including ransomware, on your endpoints and network. Using our global allowlist, we remove the work that normally comes with Application Allowlisting; a NIST recommended approach.
Access a suite of secure Remote Management Tools inside of your PC Matic Pro Cloud Console. From anywhere in the world, you can quickly VNC into a user's machine, open a Remote CMD Prompt to run scripts locally, browse and upload to file directories, remotely shut down and more.
PC Matic's Secure RDP Lifeline provides a suite of security and management tools for RDP. Introduce allowlist-based protection for RDP sessions, get real-time SMS alerting with quick actions to kill an active session, and review expansive reporting that includes IP, location, duration, device name, etc.
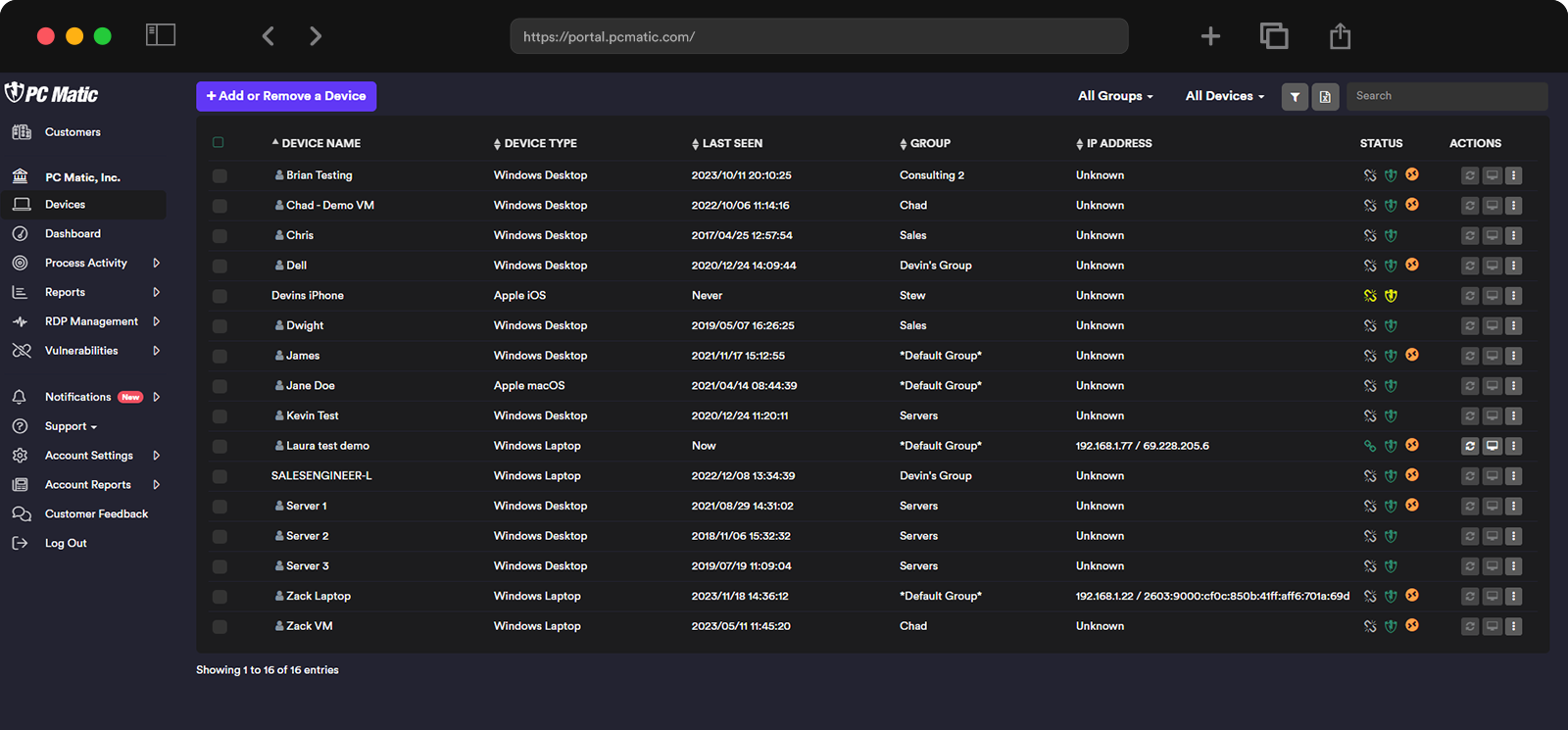
PC Matic for Small Business provides complete system security and ransomware prevention by leveraging its globally automated allowlist in combination with a suite of remote management tools. Protecting against ransomware and new types of malware requires a shift in focus. Reacting to infections after they occur is no longer an effective strategy against cybercriminals. Your security solution must block all unknown applications and only allow verified known good applications to run. With PC Matic, this is simple to deploy using our backbone of billions of known good applications and devices. In the event of a false positive, you can add an exception for custom or unique software to your entire business with just a few clicks.
Small Business Antivirus blocks cyber threats including privacy breaches, polymorphous viruses, trojans, worms, fileless infections, rootkits, spyware, adware, and fake virus scams. Save on the best small business malware protection to keep you and your data safe against threats to your sensitive data files and network system.